Refractive Errors in Children
Myopia (also known as near-sightedness)
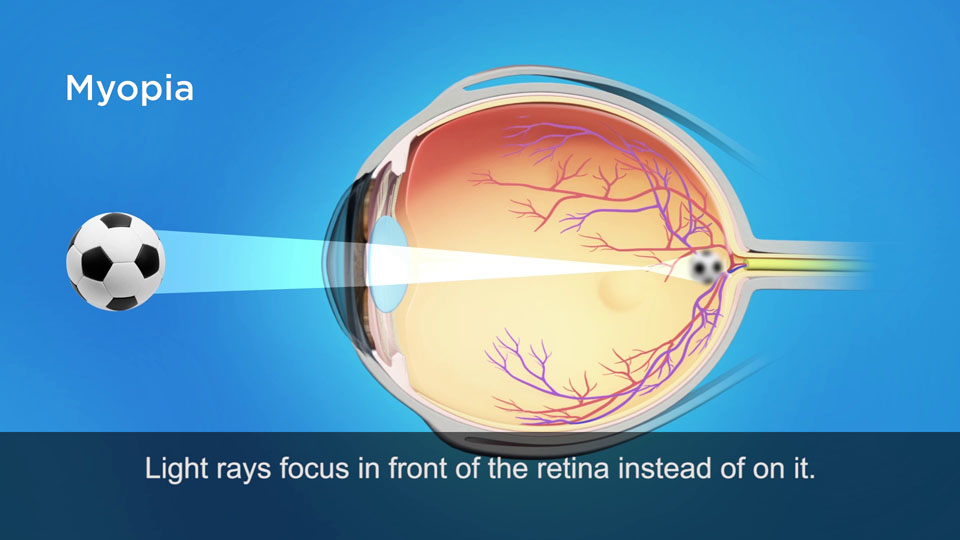
In a myopic eye, the eyeball is too long or the cornea's degree too powerful. The light rays are brought to a focal point in front of the retina, resulting in a blurred image for distance objects. Images for near remain clear.
Spending too many hours playing games on hand-held devices, watching television and reading may contribute to the development of myopia in children. Always take an eye break after 20 minutes of near work activities, or spending time on outdoor activities in daylight may reduce the risk of developing myopia.
Treatment
Children first undergo a full Ophthalmic examination which may include:
- Refraction (checking the degree of myopia in the eye's 'natural' state)
- Cyclorefraction (testing of the degree of myopia using eye drops which completely relaxes the internal muscles of the eye)
- Assessment of eye movements
- Examination of the front and back segments of the eye
- Non-contact measurement of the length of the eyeball using a special scanning laser interferometer called an optical biometer
After taking a comprehensive history and examination of the patient's eye and general health, treatment may be recommended.
Atropine 0.01% has virtually no side effects and has been shown to reduce myopia progression by 40 to 60% in local studies. Higher concentrations may also be used for cases with faster progression. Special myopia control glasses and Ortho-Keratology(OK) contact lenses use the principle of making the image seen by the eye fall either in focus on the retina or within the eyeball. It is thought that this reduces the tendency for the eye to grow longer which is what happens in myopia progression.
Hyperopia (known as far-sightedness)
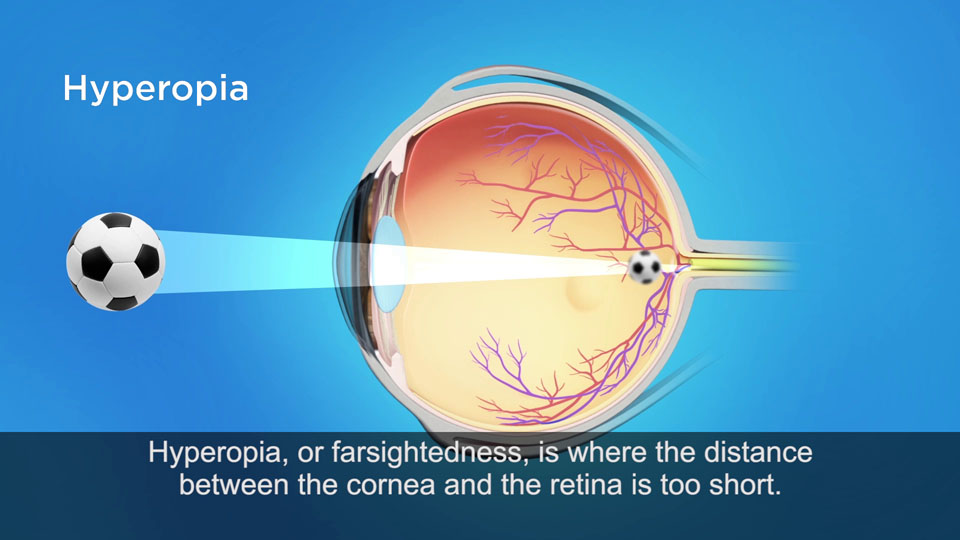
In a hyperopic eye, the eyeball is too short or the cornea is too flat. The light rays are brought to a focal point behind the retina, resulting in images which are blurry for far objects and even more blurry for near.
Most children are far-sighted, but they may not experience symptoms of blurry vision if their eyes are able to accommodate and bend light rays so that they come to focus on the retina.
Treating Amblyopia Video
Treatment
The mainstay for the correction of hyperopia is by means of spectacles. However, children with hyperopia should be screened for squints (misaligned eyes) and amblyopia (lazy eye) to ensure proper development of their visual system.
Astigmatism
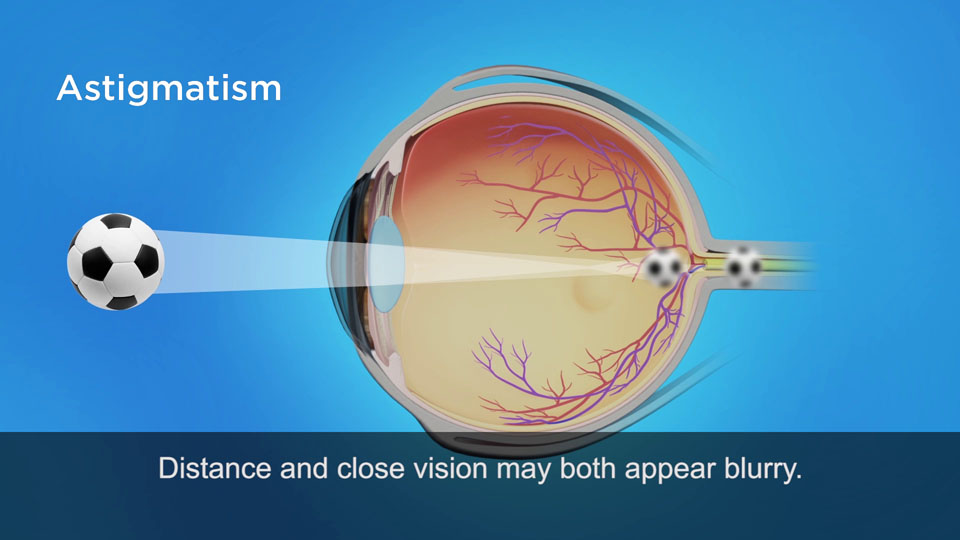
Astigmatism can occur with myopia and hyperopia. In an astigmatic eye, the cornea has an uneven curvature. Light rays do not converge to a single focal point. Instead, a portion of the light rays merge in a line in front of, or behind the retina resulting in a distorted view.
Children who have symptoms of astigmatism such as blurry vision or distorted vision may not be aware of this condition and this would affect the child's performance in school.
Treatment
The mainstay correction of astigmatism is by means of spectacles.
Symptoms of refractive errors:
- Double vision
- Glare or halos around bright lights
- Blurred vision
- Squinting
- Headaches
- Eye strain